Introduction
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a technology that enables wireless communication between devices. BLE is commonly used in IoT devices and other wearable technologies, and most many modern smartphones support it. If you’re building a Flutter app that needs to communicate with BLE devices, the flutter_blue package is a great resource. This package makes connecting to, discovering, and interacting with nearby BLE devices in Flutter easy.
Therefore, this blog highlights the basics of using flutter_blue and provides some code examples to help you get started.
Connecting to a BLE Device
The first step in communicating with a BLE device is establishing a connection. To do this, you’ll need to get the device’s Bluetooth address, which is a unique identifier for the device. You can usually find the Bluetooth address in the device’s documentation or by scanning for available devices using the flutter_blue package.
Once you have the Bluetooth address, you can use the connect method of the BluetoothDevice class to establish a connection as demonstrated below:
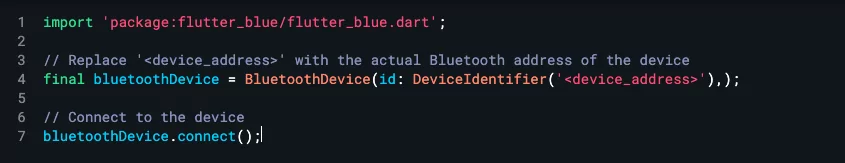
Discovering BLE Devices
If you don’t know the Bluetooth address of the device, you want to connect with, you can use the flutter_blue package to scan for available devices. Next, you’ll need to create a FlutterBlue instance and use the startScan method to start the scan. Here’s an example of how to do this:
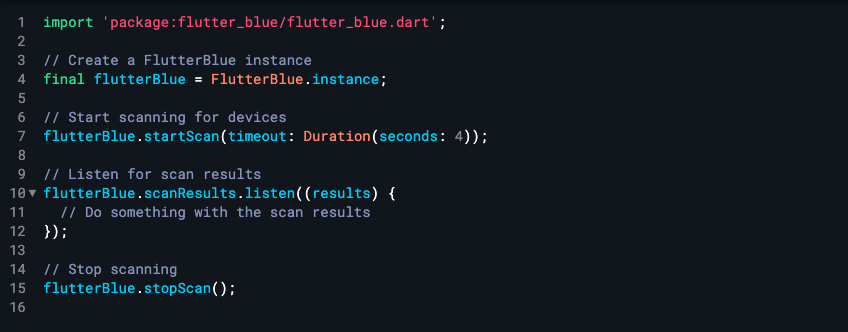
Transform your App Experience with AlphaBOLD's Flutter Expertise!
Take the next step in mobile development. Contact AlphaBOLD for innovative Flutter solutions and begin your journey to a superior app experience with a complimentary consultation.
Request a ConsultationInteracting with BLE Devices
Once you’ve established a connection with a BLE device, you can interact with it using its services and characteristics. A service is a collection of related characteristics representing a specific device aspect, such as its temperature sensor or battery status. A characteristic is a value that represents a specific aspect of the device, such as its name or manufacturer.
Looking for Mobile App Development Services
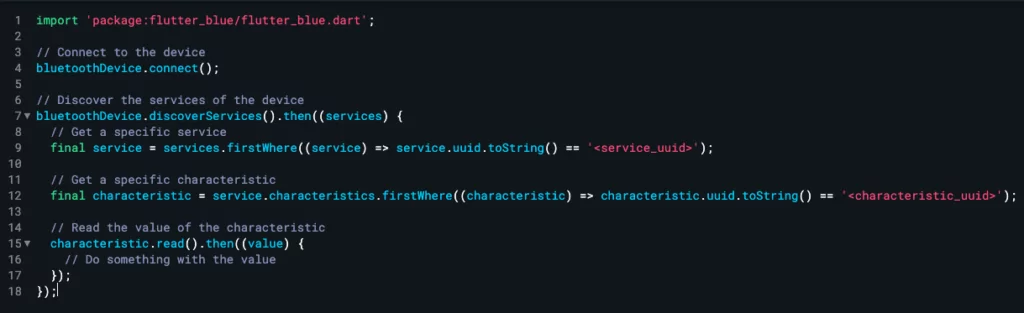
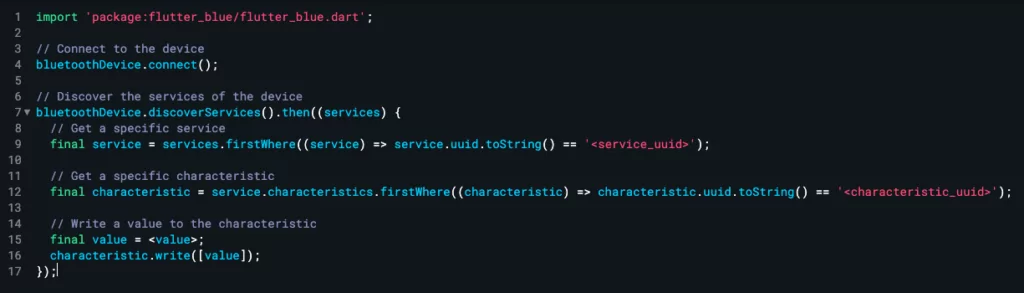
To access a service and its characteristics, you’ll need to use the discoverServices method of the BluetoothDevice class to discover the device’s services. Refer to the following:
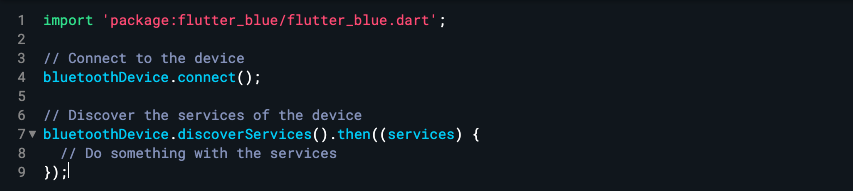
Once you have the services, you can access their characteristics using the characteristics property of the BluetoothService class. Here’s an example of how to do this:
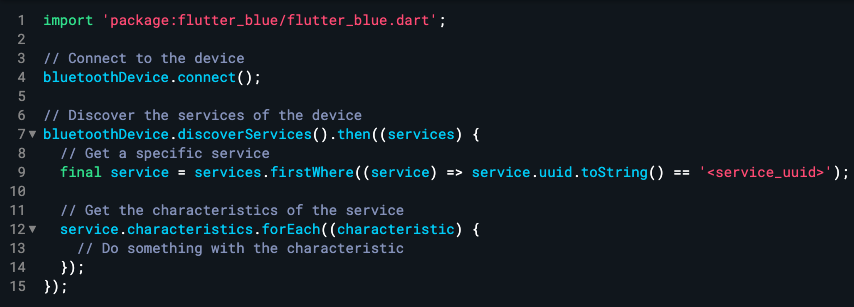
Reading and Writing Characteristics
Once you have access to a characteristic, you can read its value using the BluetoothCharacteristic class’s read method. Here’s an example of how to do this:
Elevate your Mobile Experience with AlphaBOLD's Flutter Development!
Discover how our expert Flutter development services can transform your app ideas into reality. Benefit from AlphaBOLD's comprehensive support and innovative solutions tailored to your needs.
Request a ConsultationConclusion
Connecting BLE devices with Flutter using BLE communication provides a powerful toolset for developing cross-platform mobile applications that can communicate with a wide range of BLE devices. By leveraging the FlutterBlue library, developers can easily scan for and connect to BLE devices and then communicate with them using a variety of standard BLE communication protocols.
By connecting BLE devices with Flutter, developers can create powerful mobile applications that interact with a wide range of devices, such as sensors, beacons, and wearables, and provide users with rich and interactive experiences.
Explore Recent Blog Posts








