Data democratization is the process through which an organization’s data is made available to all the employees within an organization. Because of data democratization, employees with non-technical backgrounds can collect and analyze the data themselves and learn how it works without the supervision of technical staff.
In this blog, we will learn what data democracy in an enterprise means, its advantages, and the key challenges usually faced in reaching data democracy within an organization.
What Is Data Democracy & Key Contributors of Data Democratization?
Business managers often wonder what is exactly data democracy?
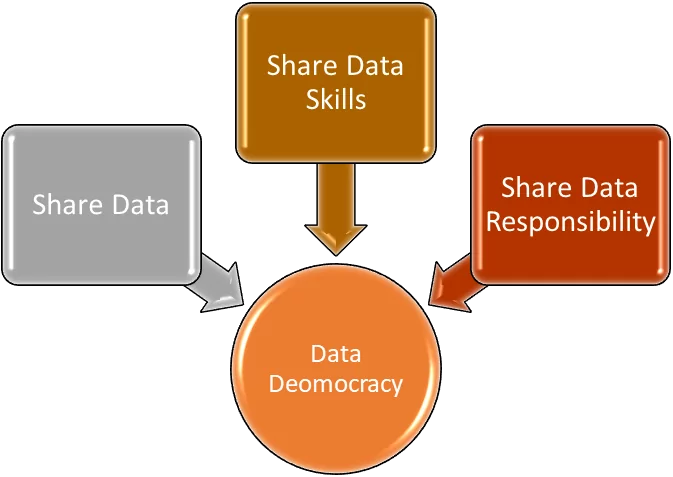
Data democracy is a framework that advocates initiatives that make data available to everyone in an organization. Ensuring data accessibility for users is a task in data democratization. There are three main components of data democratization that play a key role in making data accessible for users:
- Share Data: The first component of data democratization is sharing data. This means ensuring access to data to a wider range of people. This results in informed decisions that are data-driven. It also facilitates collaboration between teams and individuals to unlock insights that may not be apparent otherwise. Finally, it also drives innovation as people find new opportunities to solve problems
- Share Data Skills: The second component of data democracy is sharing data skills. It is essential to data democracy because it gives people the necessary data literacy and skills to get insights from the data. It also enables them to effectively understand the data and communicate with others with the help of data. Also, sharing data skills is critical to ensure the ethical use of data, such as data security and privacy.
- Share Data Responsibility: Sharing data responsibility is another critical element of data democracy. It is related to the fair use of data in an ethical and transparent manner. It states that all the stakeholders are responsible for data protection and security. In this manner, all the levels in the data hierarchy are to ensure data auditing, security compliance, and fair use of data.
Figure 1: Three Pillars of Data Democracy
Benefits of Data Democratization
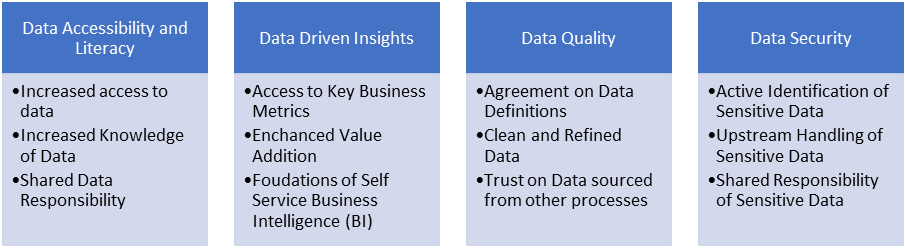
Data democratization has many benefits for an organization. It guarantees broader and easier access to data for everyone in the organization and enhances data literacy among the employees regardless of their technical background and knowledge. As a result, all the employees know how to converse in the data language, and everyone can contribute to the data-driven business culture. Data democratization forms the basis of better-equipped employees as it lays the foundation of self-service analytics. According to the latest research, data democratization within the organization better data literacy, empowerment of a broader range of employees, market awareness, better customer service, enhanced collaboration, and added value of employees. Hence, incorporating data democratization techniques into the business is the need of the hour, and organizations must know how to do it correctly.
Figure 2: Advantages of Data Democracy for Organizations
Data Democratization Challenges
Although the benefits of data democratization are unquestionable, there are challenges in implementing this process. Some of the data dimerization challenges in the implementation across an organization are:
Data in Silos
Data Silos are unintegrated repositories of data within an enterprise. They are one of the most prevalent challenges in democratizing data. The presence of data in silos hinders the discovery and usability of data throughout the organization. Therefore, enterprises need to invest in building data solutions based on single-source-of-truth architecture.
Legacy Systems
Inflexibility in legacy data systems is also a challenge in achieving data democracy. Outdated and conventional systems for data handling and analysis are generally inflexible to implement self-service Business Intelligence (BI). Also, these legacy systems hinder the democratization process by not allowing the liberating of the data. Hence, managing the legacy systems for a better data flow is crucial to data democratization.
Explore Our Data Solutions
Data Literacy Challenges among Employees
Data literacy challenges also hinder data democratization. Employees with limited or no technical knowledge about the use of data are ineligible to access data. However, this is also why data should be made available across the organization, i.e., to enhance data awareness and literacy among employees. Careful data release and better supervision can ensure data democratization and prevent poor data management while ensuring maximum data usability for all employees.
Data Security and Integrity Concerns
There is a misconception that the higher the access to data, the greater the data security risk. However, this does not have to be the case. Data democratization does not mean unregulated access to data. It ensures the proactive application of data security and privacy on upstream processes, thus reducing the probability of data leaks or security breaches. Once the data democratization process is initiated, sensitive data is tagged and identified, and relevant compliance actions can be taken to ensure data security.
Power BI: The Leading Software for Data Democratization
Power BI is a popular tool developed by Microsoft for business analytics, visualization, and sharing insights across an organization. It has certainly made strides in facilitating data democratization, but whether it’s “the best” depends on the specific requirements and context of the organization. Here’s an overview of why Power BI is often lauded for its role in data democratization:
- User-Friendly Interface: Power BI offers a intuitive drag-and-drop interface, which allows users of varying technical expertise to interact with and visualize data easily.
- Integration with Microsoft Products: Being a Microsoft product, Power BI seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft offerings like Excel, Azure, and SQL Server. This makes data sourcing and analysis streamlined for businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Data Connectivity: Power BI supports a wide range of data sources, both on-premises and cloud-based. It can connect to databases, Excel spreadsheets, cloud services like Azure, and even third-party platforms like Google Analytics.
- Interactive Dashboards and Reports: The platform allows users to create interactive reports and dashboards that can be easily shared with others. These dynamic visualizations facilitate better decision-making.
- Scalability: Power BI has both desktop and cloud-based versions. The cloud version, Power BI Service, allows for scalability and sharing across large enterprises.
- Security Features: Power BI incorporates row-level security and other advanced security features, ensuring that data remains confidential and that only authorized users can access specific data.
- Collaboration and Sharing: Users can collaborate on reports in real-time and publish dashboards that can be accessed by others in the organization. This fosters a culture of data sharing and collective decision-making.
- Cost-effective: Power BI offers competitive pricing, with even a free version (Power BI Desktop) for individual use. This makes it accessible for businesses of various sizes.
- Continuous Updates: Microsoft regularly updates Power BI with new features and capabilities, ensuring it stays relevant and powerful.
However, it’s worth noting some considerations:
- Learning Curve: While Power BI is user-friendly, mastering its more advanced features might require training.
- Performance: With large datasets, performance might sometimes be an issue, especially in the Desktop version.
- Customization: Some users might find the need for more advanced customizations which can be a bit restrictive in Power BI compared to other BI tools.
Interested in learning more about Power BI?
Explore our Power BI services!
Conclusion
Data democratization has many uses ranging from self-service BI to initiative-taking data security strategies. However, there are some concerns associated with data democracy adoption ranging from legacy systems to data literacy. Nonetheless, organizations must try to democratize their data to develop a more data-driven culture.