Introduction
Building on our previous discussion in Advanced BLE Operations series part 3, where we established the basics of BLE communication using Flutter. This blog post will dive deeper into advanced BLE operations of custom development.
Whether you’re a seasoned Flutter developer looking to expand your skill set or a newcomer eager to tackle the complexities of BLE operations, this guide will elevate your understanding and capabilities. We’ll cover a range of advanced topics, such as managing connections, handling notifications, and ensuring a robust communication flow with BLE devices using the flutter_blue package.
Managing BLE Connections For Smooth Advanced BLE Operations
Maintaining a stable connection with a BLE device is critical for ensuring seamless interaction. It’s not just about connecting; it’s about ensuring that the connection stays alive and is responsive to both the app and the device’s needs.
Reconnecting After Disconnection:
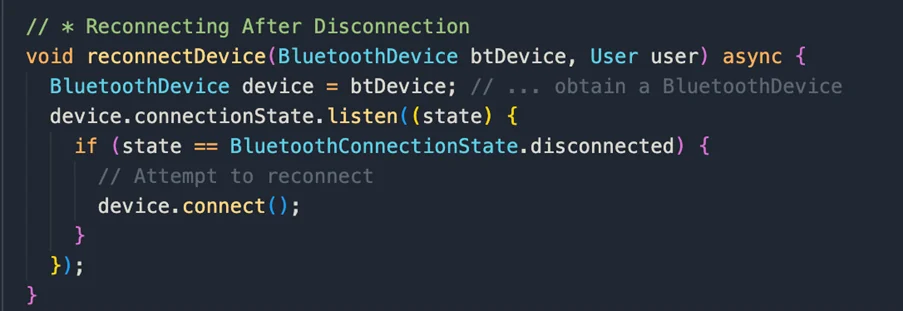
This snippet listens for changes in the device connection state. If the device gets disconnected, it automatically attempts to reconnect.
Read More: Connecting BLE Devices With Flutter (Part 2) – Bluetooth State.
Handling Connection Timeouts:
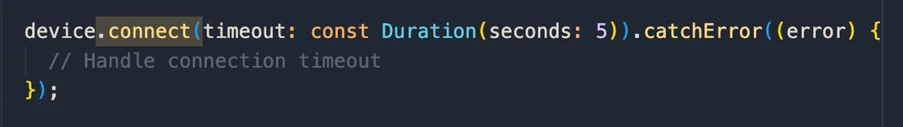
The connect method can accept a timeout parameter. This ensures that the app can handle the situation gracefully if the device doesn’t connect within the specified time frame.
Handling Notifications
In Advanced BLE Operations, notifications are a way for a device to inform the app about changes to a characteristic without the app having to read it periodically.
Subscribing to Notifications:
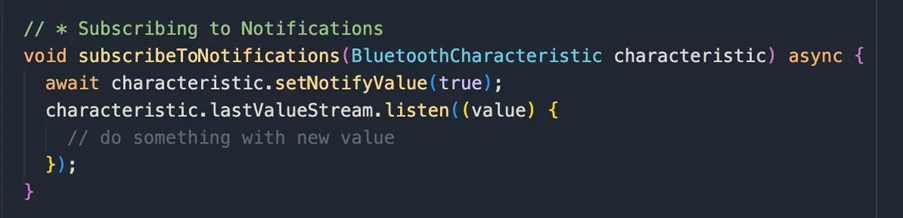
Unsubscribing from Notifications:
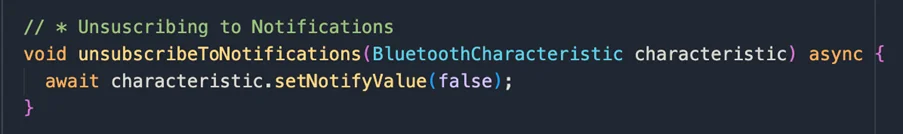
When notifications are no longer needed, it’s important to unsubscribe to save power and reduce unnecessary data transmission.
Read more: Connecting BLE Devices With Flutter (Part 3) – BLE Communication.
Reading and Writing Characteristics with Error Handling
While we covered the basic read and write operations in Part 3 of Advanced BLE Operations, handling potential errors is crucial for robust applications.
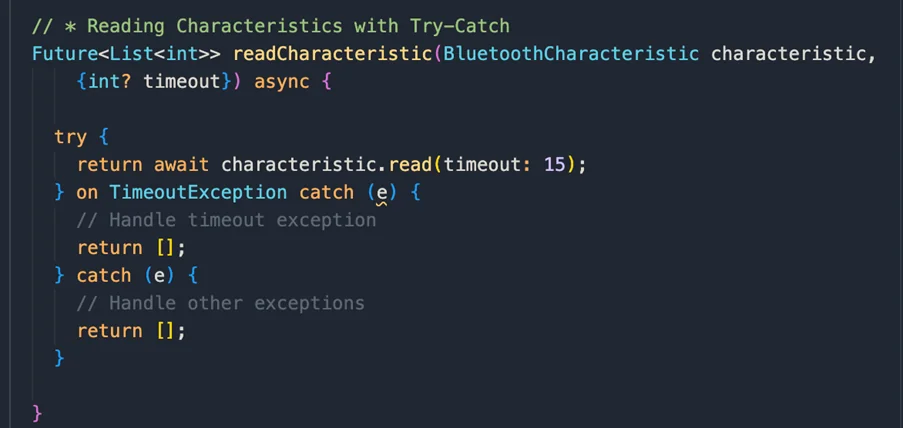
Reading Characteristics with Try-Catch:
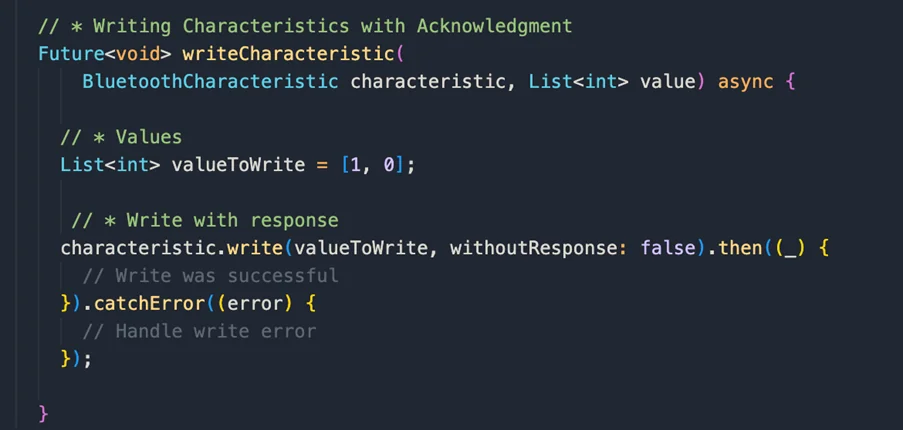
Writing Characteristics with Acknowledgment:
Want a Seamless BLE Implementation for Flutter Apps?
Delve deeper into connecting BLE devices with Flutter. If you are ready to implement these insights in your app, connect with AlphaBOLD for custom development expert guidance and seamless BLE implementation.
Request a consultationConclusion
We have taken our BLE operations a notch higher in this series installment, integrating advanced techniques for managing connections and handling notifications. These practices are essential for creating a stable and reliable communication channel between your Flutter app and BLE devices.
As always, we encourage you to experiment with these snippets and integrate them into your application logic. For our next Advanced BLE Operations series, we will look at troubleshooting common BLE issues and optimizing the BLE communication for better performance and user experience.
Stay tuned and keep coding! Feel free to reach out if you have any questions or topics, you would like us to cover. Your feedback drives our content. Thank you for following along in our BLE with Flutter series!
Explore Recent Blog Posts






