Introduction
Customization and configurability come across as business requirements, which are a little tricky to implement. We need a scalable, reusable, and robust method for varying business models and requirements, which require minimal changes in the existing code. In a web application, forms represent the exchange of data between the system and its users. The form fields which represent data can be dynamic in different circumstances. The modern web application uses API-driven architecture. Applications leverage customization and configurability using this architecture. This customization also has some impact on the implementation of certain modules in the application. For example, the same module/screen of an application can have different form fields depending on business requirements or location. In order to cater to these varying models, dynamic forms are used. In Angular, this is enabled by Reactive Forms.
There are two kinds of forms in Angular:
- Template-driven forms
- Reactive forms
For the purpose of this article, we will be exploring Reactive Forms only.
Forms in Angular have three base classes:
- FormControl tracks the value & validation status of an individual form control.
- FormGroup tracks the same values & status for a collection of form controls.
- FormArray tracks the same values and status for an array of form controls.
In the example we are going to explain, we are only going to use FormControl and FormGroup.
Explore Dynamics 365 Customer Engagement
Evaluating CRM options for your business? Learn more about Microsoft's CRM Solutions, a product suite called Dynamics 365 Customer Engagement.
Request a ConsultationDynamic Contact Form Using Reactive Forms
Let us assume we have a page where we must take contact information from users. Business requirements are such that if a user accesses the page from a certain locality, the user must input the address in addition to the other contact fields on the form.
We can implement this using Reactive Forms. Let’s dive into the code to make it possible. We are going to use the following steps in our existing code.
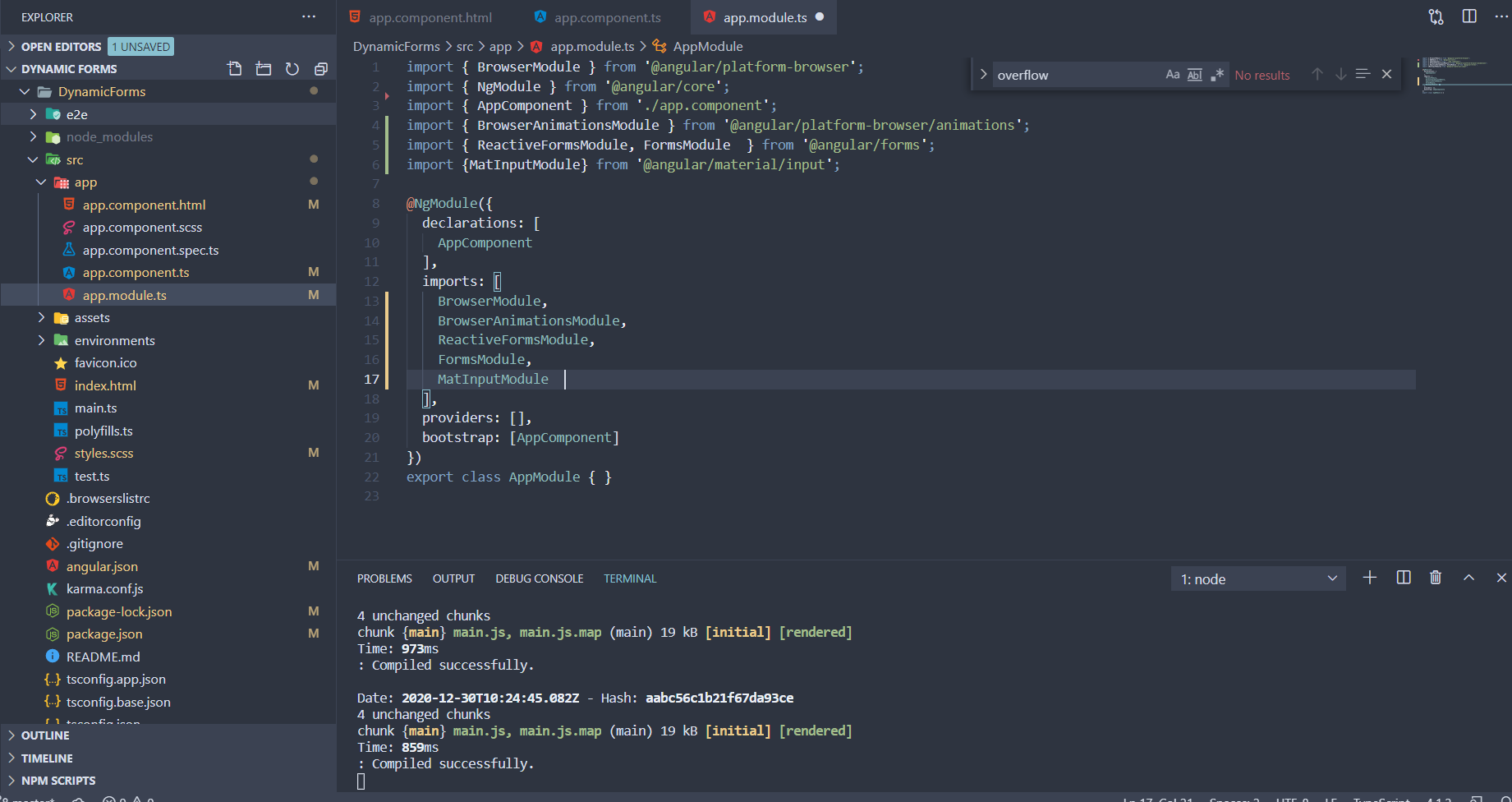
1. Import Reactive Forms Module in Dynamic Forms Project:
Import ReactiveFormsModule and FormsModule in our application
2. Import FormGroup and Form Control in app.component.ts:
Import FormGroup and FormControl in our app.component.ts file
import { FormControl, FormGroup } from ’@angular/forms’;
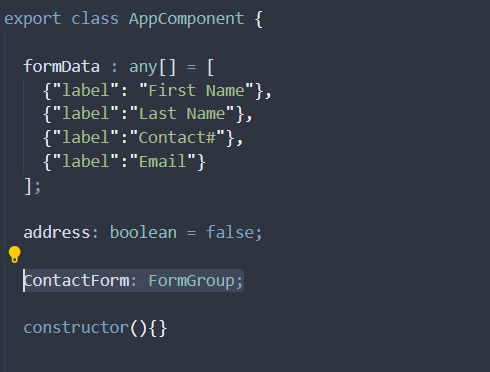
3. Create FormGroup in app.component Class:
Create a form group named ContactForm in our AppComponent class
Along with the Form Group, we have initialized a boolean variable address (which we will provide to a function to mimic the specific location functionality for a user) and a json object array, formData, for our fields, which the form will populate on the go. Remember! In the real world, this data may come from an API call or some other source. The idea is to simulate a real-world scenario for this ‘reactive forms’ blog!
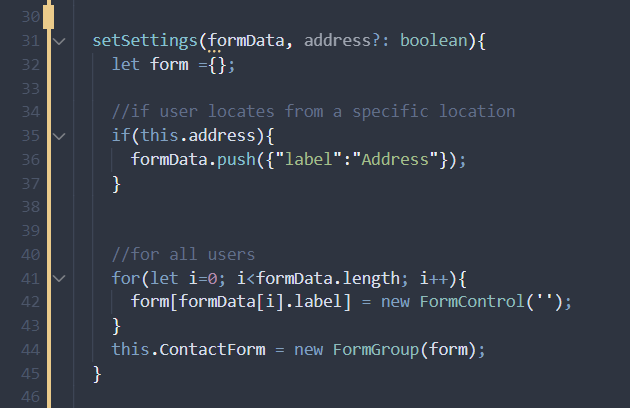
4. Create a Function in app.component.ts:
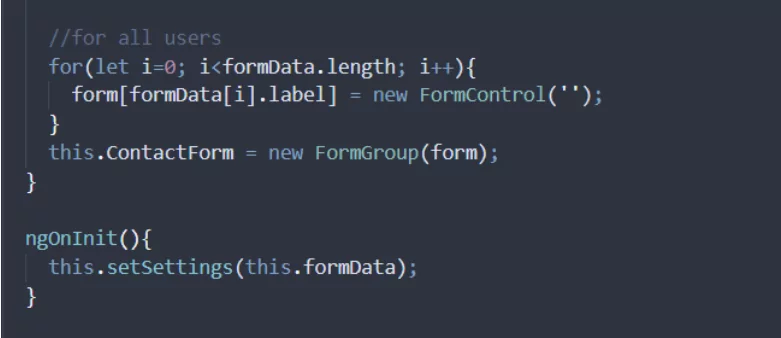
Create a setSettings function that will populate the form fields dynamically. In this function, we are passing two parameters, formData and address.
Explanation:
In setSettings function, we do the following:
- Check if the user is from a specific location or not, and if he is, we add a new field to our formData.
- Loopthrough formData array and create a new form control and assign it to form object.
- We populate our FormGroup, ContactForm.
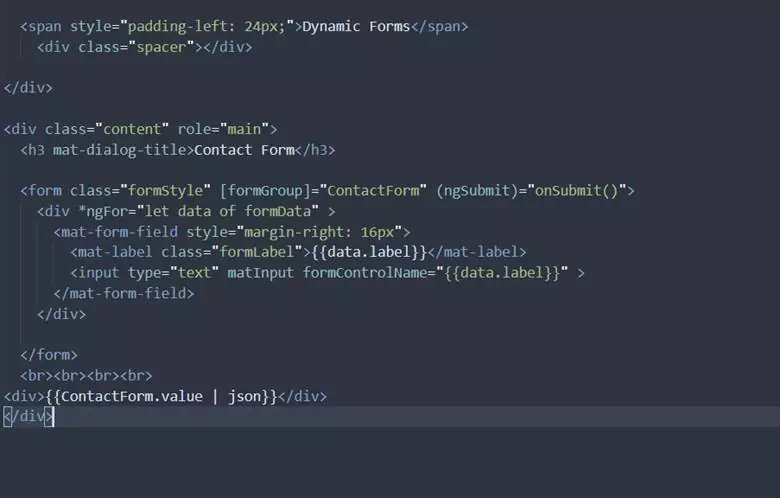
5. Dynamic Forms Template File Changes in app.component.html:
In our app.component.html file, we have the following code:
Explanation:
- [formGroup] directive to refer to our ContactForm, which we created and populated.
- *ngFor directive to loop through our formData and layout corresponding fields, respectively.
- formControlName synchronizes a FormControl in an existing FormGroup to a form control element by name. In our case, it refers to thedynamic form fields we have defined in the formData object array.
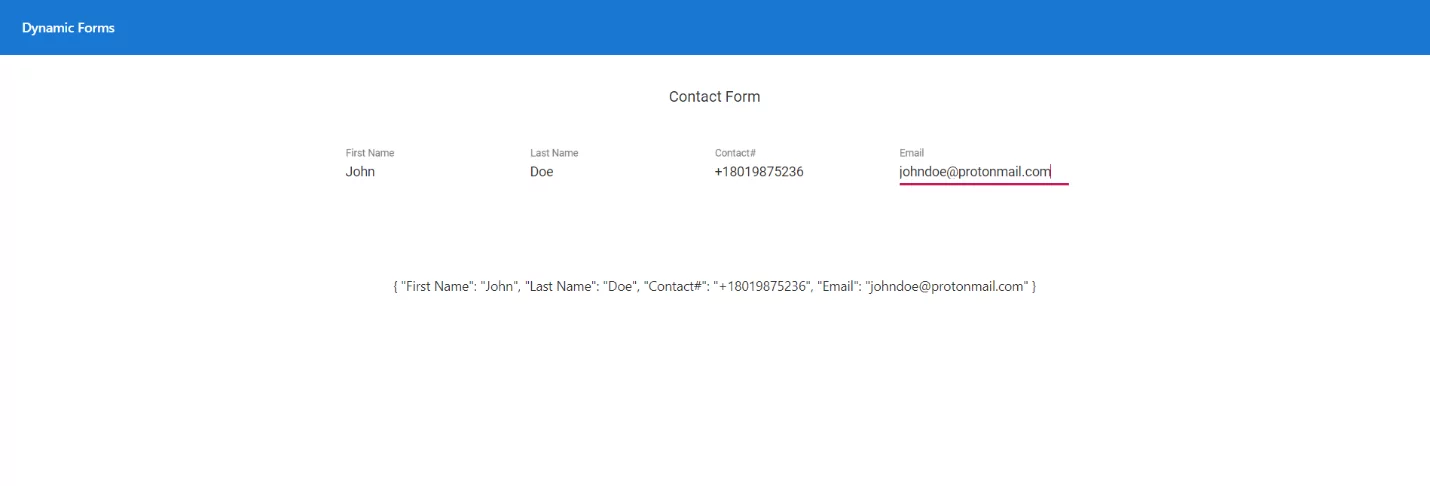
- We have displayed the ContactForm value at the end of our page to show the values as we input them.
Read More: Angular Vs. React: Which Is A Better JavaScript Framework?
6. In the End, We have to Call Our setSettings Function in ngOnInit():
That is it. If we run the project, we will see the following fields on the screen that have been added dynamically in our reactive form.
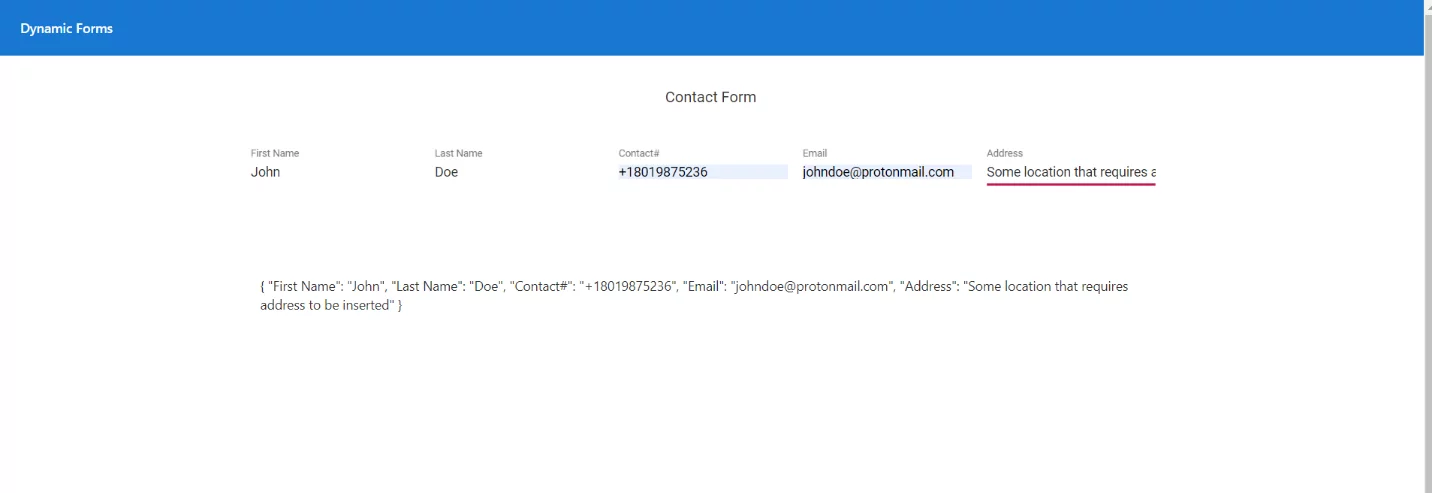
Now assume a person accesses our page from a specific location. Our business requirements demand address in the contact form. We do not have to change anything in the existing code or create a separate form to cater to this requirement. We have to change the model, and the reactive form will automatically ‘react’ to the new model and display the new field.
Now let’s assign the value ‘true’ to our address variable and see what happens.
address: boolean = true;
You can see that our dynamic forms have responded to a change in the model.
Elevate Your Angular Development Expertise
Uncover the full potential of dynamic (reactive) forms in Angular. Explore AlphaBOLD's Custome Development Services to enhance your form-building capabilities. Transform your Angular forms with us!
Request a ConsultationConclusion
Explore Recent Blog Posts