Introduction
Choosing the right ETL Tool for data integration and migration processes can be confusing. Professionals always want to choose the tool to give them the best possible results. This blog will discuss two important tools, Azure Data Factory, and SQL Server Integration Services, and their differences, which will help you decide what best fits your requirements.
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)
SSIS is a flexible and fast data warehouse tool used for extracting, integrating, and transforming data. It is used to execute a wide range of data migration tasks as it provides users with a platform to move data from one source to another in an easier manner providing them with complete control to design ETL according to their requirements. SSIS supports a wide range of data sources like SQL Databases, Oracle Databases, Excel Files, DB2 Databases, etc. It helps you to create solutions without writing a single line of code.
Learn more about Azure DevOps Services
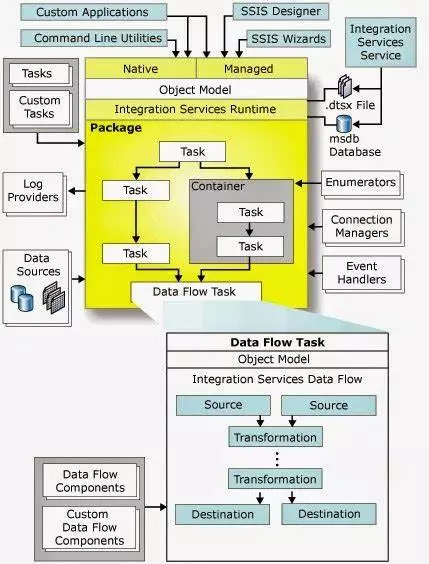
SSIS has four important components:
- Control Flow: It is the brain of the SSIS package. It helps to arrange the order of all the components, such as containers, tasks, etc.
- Data Flow: If Control Flow is the brain, Data Flow is the heart of the SSIS Package. It allows you to extract, transform and then load data into another destination.
- Packages: Packages are the collection of Control and Data Flow. The containers and data flow tasks in the control flow, and the sources and destinations in the data flow are known as packages.
- Parameters: These are special types of variables. They help to ease the process of passing run-time values to SSIS packages.
Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory is a cloud based ETL service for data integration and data migrations. It enables users to develop data-driven processes to orchestrate data movement and transformations. Azure Data Factory helps you to create and schedule pipelines that can get data from several different data sources. It is also used to give meaning to big data stored in a storage system by helping in data movement and performing transformations on big-scale data.
Read more: Introduction to Azure Data Factory
Start your Cloud-based Data Integration Journey Today!
Leverage the power of Azure Data Factory (ADF) to streamline your data integration processes and unlock valuable insights from your data. Embrace the future of data management by allowing us to guide you through every step of your data integration journey.
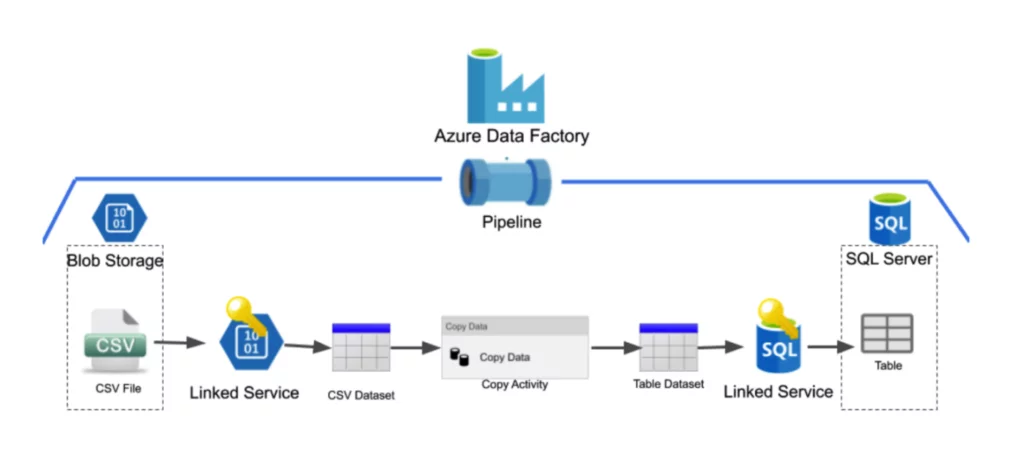
Request a ConsultationADF has Four Key Components:
- Pipeline: Contains the tasks you want to execute. It defines the complete workflow, such as what tasks should be performed and in which order.
- Activity: These are the individual steps inside a pipeline, where each activity performs a single task. They can either be chained or run in a parallel manner. They control the flow inside a pipeline.
- Datasets: Collected data is required as input for the ETL process. These are views that represent databases, files, or folders.
- Linked Services: These are the connection strings used to connect data sources and services and authenticate them.
Azure Data Factory vs SSIS
Both of these tools have similar descriptions, as they were created for the same purpose. But to understand their differences, let’s compare them.
Learning Curve:
Both tools are easy to learn and to perform simple tasks. However, to master any new software, a lot of time and practice are required. SSIS has been around for a long time. It is a mature software with few major changes in the past few years. These slower evolutions make it less of a moving target, making it easier to learn than Azure Data Factory. Also, SSIS is well-documented owing to its age, which gives it a little advantage over ADF.
ADF, on the other hand, is still evolving. More features and capabilities are yet to be released. Still, if you already have some SSIS knowledge, it is much easier to learn with the help of the available digital training materials and documentation.
Data Variety:
SSIS deals with structured data, which includes a wide range of databases like SQL servers, Oracle, DB2, etc. However, it does not integrate with new file formats like JSON, Parquet, etc. You can use third-party C# connectors or script components for JSON, RestAPIs, etc.
Azure Data Factory can deal with both structured and unstructured data. It can connect to over 90+ sources, including SQL and No SQL Databases, RestAPIs, SaaS Platforms, etc. It supports nearly 20 data warehouses and database destinations in the cloud and on-premises.
Data Velocity:
SSIS is a batch-processing ETL tool. It performs this by grouping the rows to be processed in batches, then processes each batch and updates each group as processed. For real-time data streams, you can develop custom triggers in SSIS.
ADF supports both Batch and Stream Processing. It can process data based on events happening in storage accounts, such as deletion or arrival of files. It also supports tumbling window triggers where you can pass the start and end times for each time window in your query, and it will process and return the data between that interval. In addition to these, ADF also supports batch triggers.
Programmability:
SSIS has a programming SDK. It allows developers to write their own code to define their connection objects, tasks, log providers, and transformations. It features a programmable object model that allows developers to create, store, and load packages using BIML and create, destroy, and modify any contained objects.
On the other hand, ADF does not have a native programming SDK, but it has automation using PowerShell without involving any third-party components. You can also use methods like .NET SDK, RestAPIs, and Python SDKs to run your pipelines manually.
Pricing:
SSIS comes as a part of the SQL Server License. The pricing is free for Express and Developer editions, but Enterprise costs $14,256 per core.
Azure Data Factory provides services at pay-as-you-go pricing. It is calculated based on the number of pipeline orchestration runs, data flow execution and debugging, and the number of data factory operations, such as pipeline monitoring.
Pros and Cons
SQL Server Integration Service:
Pros:
- Able to handle data from a variety of data sources.
- Provides transformation functionality.
- C# or VBA can be used to extend its functionality.
- Easy to learn and user-friendly.
- Debugging capabilities are great, particularly during flow execution.
Cons:
- Package execution reports can only be seen through Management Studio.
- Running multiple packages in parallel is difficult. Slow Evolution.
- Working with unstructured datasets might be difficult.
Azure Data Factory:
Pros:
- It provides a server-less solution, eliminating the mundane tasks of maintaining and updating software.
- Supports integration with multiple 3rd party connectors.
- Supports long and time-consuming queries.
- Highly scalable and cost-effective.
- Creating pipeline schedules is much easier.
Cons:
- Less native transform functions as compared to SSIS.
- Does not have intelligence or debugging tools.
- Needs to maintain perfect billing strategy or else will lead to excessive cost.
- Lack of flexibility compared to other ETL tools, e.g., C# script component.
Read more: Automate ML Models Deployment with Azure Services
Optimize your Data Processes with Azure's Power!
AlphaBOLD is here to assist you in leveraging Azure's full potential to streamline your data integration, analytics, and intelligence operations.With our expertise, transform your data into a strategic asset that drives decision-making and fosters innovation.
Request a ConsultationConclusion
SSIS and ADF are both highly capable ETL tools. Each one can succeed when used properly. SSIS would work well for you if your workload is mostly on-prem or ETL processes run consistently throughout the day. But if you only want to pay for the resources used and most of your workload is in the cloud, then ADF is a suitable choice. Considering the factors discussed above and what your project requires, you can decide which is the right tool for the job, whether SSIS, ADF, or a hybrid.
Explore Recent Blog Posts








